Lipid homeostasis
Is lipid metabolism in the cell also out of balance in pain conditions? In other words: Can a balanced lipid metabolism enhance pain resolution? Many individual factors contribute to lipid metabolism: Binding proteins, transport proteins or enzymes responsible for binding of fat molecules such as cholesterol, for transporting them through cell membranes and catalyzing their degradation and remodeling. A mismatch of single factors can affect excitability of pain receptors and thereby contribute to neuropathy.
ApoA1/HDL and ABCA1
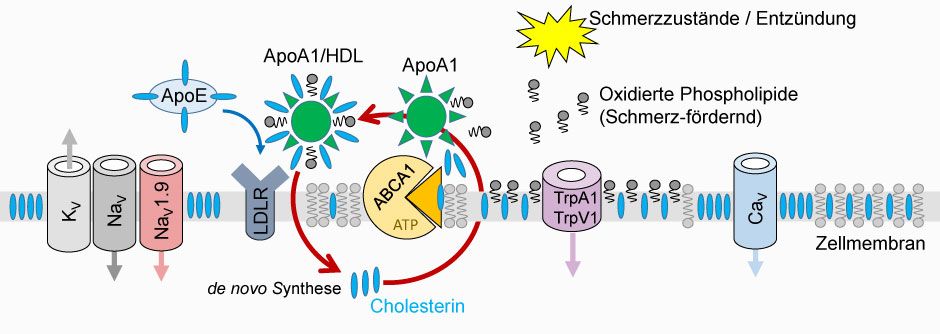
Project 9 of ResolvePAIN will focus on the function of apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1) and the transport protein ABCA1 in pain development and resolution of pain. ApoA1 is an important component of high- density lipoprotein (HDL) and holds the HDL molecule and its components together. ABCA1 transports cholesterol and phospholipids from inside the cell to the cell surface, where they are partly incorporated into the cell membrane or become part of HDL-like particles. The quantitative and qualitative content of cholesterol and phospholipids in the cell membrane influences the activity of ion channels and thus affects pain stimuli.
Approach
The mode of action and principles of lipid proteins will be investigated using cultured ‘pain receptors’, so-called nociceptors. Here, the focus is on methods that record the excitability of the pain receptors. Furthermore, we investigate animal models carrying a chronic nerve ligation to find out how cell profiles, apolipoproteins and ABC transporters change quantitatively and qualitatively during the development and resolution of neuropathic pain. To validate the hypotheses, inducible, cell type-specific ABCA1 knockout mice will be developed - animals in which ABCA1-encoding genes in pain receptors have been selectively inactivated.
Translational research
In a translational approach, the correlation between pain relief and serum ApoA/HDL cholesterol profiles will be investigated in patients with complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) and chronic postoperative groin pain.
Significance
Preliminary data already indicate that the cellular cholesterol transporter ABCA1, as a key element in the regulation of apolipoprotein A1 and HDL, plays a central role in pain development and pain resolution. If this can be confirmed, therapeutic strategies that promote natural, endogenous mechanisms of pain resolution could be tested.
In this project, we will also develop and test mouse models to study pain relief and resolution for other projects such as P6.
Research Team P9
Head
Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Robert Blum
University Hospital Würzburg
Prof. Dr. Alexander Brack, MD
University Hospital Würzburg
Members of the team
Dr. rer. nat. Annemarie Sodmann
Felicitas Schlott, PhD Student
Selected publications
Oehler B, Brack A, Blum R, Rittner H (2021)
Pain Control by Targeting Oxidized Phospholipids: Functions, Mechanisms, Perspectives.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2021 Jan 25; 11: 613868. doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.613868
Go to publication
Segebarth D, Griebel M, Stein N, R von Collenberg C, Martin C, Fiedler D, Comeras LB, Sah A, Schoeffler V, Lüffe T, Dürr A, Gupta R, Sasi M, Lillesaar C, Lange MD, Tasan RO, Singewald N, Pape HC, Flath CM, Blum R. (2020)
On the objectivity, reliability, and validity of deep learning enabled bioimage analyses.
Elife. 2020 Oct 19; 9: e59780
Go to publication
Oehler B, Kistner K, Martin C, Schiller J, Mayer R, Mohammadi M, Sauer RS, Filipovic MR, Nieto FR, Kloka J, Pflücke D, Hill K, Schaefer M, Malcangio M, Reeh PW, Brack A, Blum R, Rittner HL (2017)
Inflammatory pain control by blocking oxidized phospholipid-mediated TRP channel activation.
Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 14; 7 (1): 5447
Go to publication
Martin C, Stoffer C, Mohammadi M, Hugo J, Leipold E, Oehler B, Rittner HL, Blum R (2018)
NaV1.9 Potentiates Oxidized Phospholipid-Induced TRP Responses Only under Inflammatory Conditions.
Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Jan 23; 11:7
Go to publication